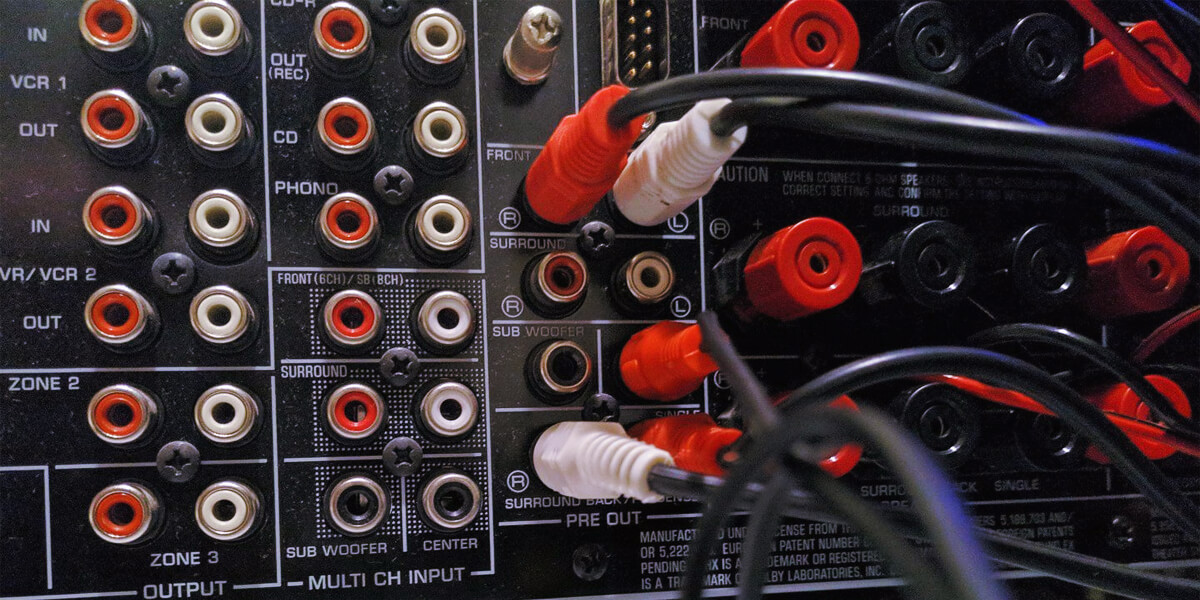
All AV receivers have built-in amplifiers to improve the sound quality. Still, these amps are often insufficient for achieving the desired sound, so external amplifiers sometimes appear necessary.
What is a pre-out on an AV receiver? It’s a connection port on the device, which makes it possible to use external amplifiers. From my article, you will get detailed information on pre-outs’ nature, their types, and ways to use them with your audio system.
What are pre-outs?
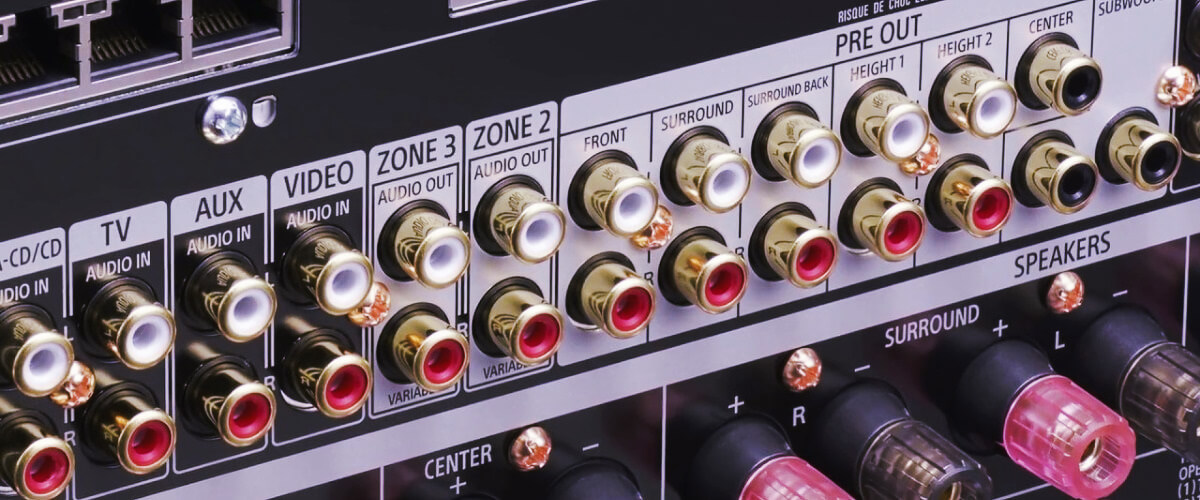

The definition
Pre-outs, short for preamplifier outputs, are audio connections found on audio/video receivers and amplifiers. They are designed to provide a separate signal output that can be connected to external audio components, such as additional power amplifiers or subwoofers.
How do they work?
Pre-outs work by providing a line-level audio signal that can be sent to external audio components for further amplification or processing. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how pre-outs function in an audio system:
- External Component Connection: To utilize the pre-outs, you connect the corresponding pre-out on the receiver to the input of an external amplifier or subwoofer.
- Line-Level Signal Generation: Processing the audio signal, adjusting its volume, tone, and other parameters, and, finally, generating a line-level signal.
- External Component Amplification or Processing: The line-level signal from the pre-out is received by the external component, which then amplifies the signal using a power amplifier.
- Speaker or Subwoofer Connection: Finally, the amplified or processed signal from the external component is sent to the speakers or subwoofer.
Types of pre-outs
There are several types of pre-outs commonly found in audio equipment:
- Main Pre-Outs: Are designed to connect to external power amplifiers that drive the main front speakers.
- Center Pre-Out: Some receivers or amplifiers have a dedicated pre-out for the center channel.
- Surround Pre-Outs: For surround sound systems, there may be pre-outs for the surround channels, such as left surround and right surround pre-outs.
- Zone 2 or Zone B Pre-Outs: These pre-outs allow you to connect external amplifiers and speakers in a separate room or zone.
- Subwoofer Pre-Out:This pre-out provides a low-frequency line-level signal that is sent to the subwoofer, allowing you to enhance the bass performance in your audio system.
The availability and configuration of pre-outs can vary depending on the specific audio equipment and its intended purpose.
Pre-outs’ pros and cons
While having these obvious benefits, pre-outs are also about certain disadvantages. For the sake of clarity, I have made a table.
| The benefits of pre-outs’ usage | The shortcomings of pre-outs’ usage |
|---|---|
| More control over your audio system | Additional cost |
| More opportunities and greater flexibility in setting up your sound | The principles of setting up may appear too complex to understand |
| Some of your room space might need to be sacrificed |
As you can see, the equipment’s increased control and configuration capabilities require additional costs and may be too complicated for beginners.
Cases when you need to use an external amplifier

There are several scenarios where using an external amplifier in conjunction with your audio equipment can be beneficial:
- Higher Power Requirements: If you have speakers that require a higher level of power than your receiver can provide, connecting an external power amplifier is rational.
- Enhanced Performance: External amplifiers usually offer higher-quality components and better power handling capabilities, resulting in improved dynamics, clarity, and detail in the auAmpingdio reproduction.
- Bi- or Tri-Amping: Using separate amplifiers for high- and low- or for high-, mid-, and low-frequency ranges naturally requires more power and a more advanced sound setup.
- Multiple Zones: The usage of an external amplifier is also rational if you’re going to have audio playback in different zones of your home.
- Dedicated Subwoofer: When you have multiple subwoofers or desire more control over the bass reproduction, using an external amplifier for subwoofers can provide greater flexibility and power.
- System Expansion: Adding an external amplifier allows you to expand your system without relying solely on the built-in amplification of your receiver or amplifier.
The procedure of connecting an external amplifier to your AV receiver
To connect an external amplifier to your AV receiver, follow these steps:
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Determine Compatibility | Ensure that both your AV receiver and the external amplifier have the necessary pre-out and input connections. |
| 2 | Gather the cables | Obtain the appropriate cables based on the available connections on your receiver and amplifier. |
| 3 | Power Off and Disconnect | Turn off your AV receiver and the external amplifier. Unplug both devices from the power source for safety. |
| 4 | Locate the Pre-Outs | Identify the pre-outs you will use based on your specific setup requirements (e.g., front left and right pre-outs, subwoofer pre-out). |
| 5 | Connect the Pre-Outs | Take one end of an RCA cable and plug the left channel (usually color-coded white) into the left pre-out of your receiver. Repeat this process for the right channel. |
| 6 | Additional Channels | If your amplifier has multiple channels and you are connecting them (e.g., for surround sound), repeat step 5 for each channel. |
| 7 | Subwoofer Connection | Connect the subwoofer pre-out on the receiver to the input on the subwoofer using an RCA cable. |
| 8 | Power On and Test | Once all the connections are secure, plug in your AV receiver and the external amplifier to power sources. |
Remember to consult the user manuals for your specific AV receiver with pre-outs and amplifier for any model-specific instructions or considerations, and take safety precautions while working with electrical equipment.
How to choose an external amplifier properly
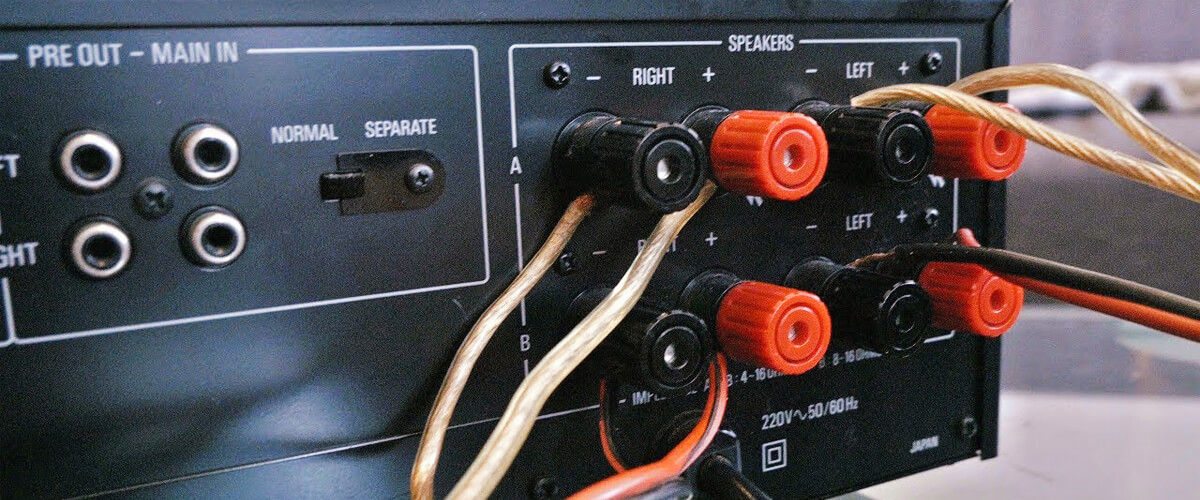
When choosing an external amplifier, I recommend considering the next factors:
- Power Output and Impedance: Consider the impedance rating of your speakers and ensure that the amplifier can handle that impedance without difficulty.
- Number of Channels: Determine how many channels you need to amplify. If you have a standard 5.1 or 7.1 surround sound setup, a 5 or 7-channel amplifier is typically sufficient.
- Amplifier Class and Technology: Different amplifier classes (such as Class A, Class AB, and Class D) have varying characteristics in terms of efficiency, power consumption, and sound quality.
- Connectivity Options: Most common options are RCA (phono) connections, but some amplifiers may offer XLR, balanced, or other specialized connectors.
- Size and Form Factor: Consider the physical size and form factor of the amplifier. Ensure it fits in your available space and can be properly ventilated to prevent overheating.
- Brand and Reputation: Look for reviews, user experiences, and professional opinions to assess the reliability of the amplifier. I recommend choosing an amplifier of the same brand as the speakers.
- Budget: Set a budget for your external amplifier and consider the price range that fits within your financial constraints.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select an external amplifier that complements your AV receiver with preamp outputs, matches your audio system requirements, and provides an enhanced audio experience.
FAQ
How do I know if my speakers require an external amplifier?
You will certainly need an external amplifier in these cases:
- When your speakers require more power than your receiver can provide.
- In case you use separate amps for different frequency ranges.
- If you have a multi-room audio setup.
- When you have a custom home theater with unique speaker configurations.
Do all AV receivers have pre-outs?
No, not all of them have this option. It’s the prerogative of more expensive models, while cheaper ones are usually deprived of the function of a pre-out port in an AV receiver.
What is the difference between a pre-out and a line-out?
Pre-outs are used for external amplification of an audio system, while line-outs connect devices with built-in amplification for audio recording purposes.